Over last decade half the contingent workforce has become increasingly important and a strategic part of the total workforce of many enterprises that collectively spend billions of dollars on this category at a global level. Managing such a large spend effectively, which on average is often 15-20% of the total spend of enterprises, specifically the IT/ITES companies, becomes critical.
An effective management of contingent workforce requires one to achieve a consistently fine balance between seemingly opposing forces or objectives – cost, risk (availability) and controls (both internal external).
Unlike other categories, contingent workforce category turns out to be significantly different and very complex to manage in that, it deals with human beings as resources. Hence the traditional supply chain factors such as inventory, perfect order, delivery lead time etc. of manufacturing or call volume, first contact resolution etc. of services sector do not directly fit to this category. Nevertheless, with some variations supply chain best practices can be applied to dramatically improve management of the category.
Some of the typical challenges that the companies face, are as below. Although these are common problems across industries, specifically for software Industry, complexity increases due to two critical factors – need for specialized skills on a regular basis and continually changing landscape of the required skills.
- Lack of Visibility into demand side of resources.
- Poor Cost Management due to dynamic needs.
- Large Supplier Base – commodity skills to niche, variety of experience levels and specializations, large service providers to boutique ones, global local players etc.
- Long Hiring or Fulfillment Cycle Time – even with a standard job description, each worker is different, making standardization inventory difficult.
- Inefficient Processes – new breed of tools and programs available in the market place are still catching up with dynamic nature of the beast.
- Exposure to Risks – co-employment, workers-comp, local labor laws etc.
- Talent Quality – especially for software industry, this is a big struggle.
- Lack of Leverage – wage increases due to factors as inflation, talent retention etc.
In our view, two factors are critical to the success of effectively managing this category –
- Procurement team owns manages not only the source to contract process but also the operations of talent supply chain. We see in many organizations, lot many internal groups get “involved” in what is called contingent workforce management, none own the end-to-end program, which is a critical success factor.Why must procurement team own end-to-end program? Procuring labor represents a complex challenge with many moving parts and stakeholders who are often at odds. For software industry, this process becomes further complex due to issues identified earlier. So, which group other than procurement team has the best setup to manage the key factors – compliance, visibility cost control. These challenges align exactly with the value that procurement delivers to the organization.
- With many moving parts and stakeholders within the organization and outside, a rigorous stakeholder or demand side management becomes key to success. Procurement team must develop a deep understanding of the company’s products/services and the impact of contingent workforce on productivity and product quality. Procurement must be able to manage all sources of talent – from TM based labor to SOW contracts with a strategic plan to broaden capacity.Finally, in applying supply chain rigor to this process, procurement team must put in use below critical elements –
- Data Capture Analytics – conducting a detailed discovery is must before venturing for a strategic plan. One must consider items such as resource classification, risk mitigation, cost drivers, reporting mechanisms etc. for gainful insights.
- Managing Details – identifying business value drivers and aligning technology outsourcing capabilities are crucial. This should culminate into establishing a seamless and robust end-to-end process.
- Road map for Success – Finally, procurement must consistently reinforce its value using smart data and performance-based metrics that will help build credibility with the internal stakeholders and help strengthen relationships and outcome. When procurement has a seat at the table, everyone wins.
Following case study from our previous work will substantiate the above –
Case Illustration – Company X
A critical category from company X’s operations perspective that comes close to direct material category –
- Impacts larger software development organization through overall workforce management. Company X deploys over 1500 contingent workers globally.
- Includes highly skilled product development resources that augment in-house skills.
- A relatively new category with evolving best practices.
At this company, significant work has been done by procurement team over 5 years period to develop series of sourcing operations best practices that helped company gain significant competitive advantage in this category. These practices have been implemented at global level
For simplicity, various best practices have been bundled into 3 major buckets –
- Stakeholder Management
- Supplier Relationship Management
- Supplier Consolidation – This time-tested practice of supply management was very effective in optimizing global supply base to under 15 from over 100 in 2010.
- Strategic Supplier Framework – A detailed frame work was developed to engage with right set of suppliers that is aligned with company’s long-term technology road map. This improved supply base performance as well as cost competitiveness significantly.
- Performance criteria was based on four key attributes – fulfillment cycle time, quality of deliverables, delivery timelines and account management.
- Business value-adds – Several improvement areas were introduced to help product units become more efficient effective, such as BOT model for healthy pipeline etc.
- Improved connect with strategic suppliers – Apart from leading traditional business reviews, Procurement team was also instrumental in strengthening the value delivery, in the form of a deeper connect with supplier’s technology practice groups.
- Rate Card Management
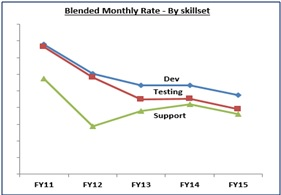
- Operations (Contingent Labor – Life Cycle Management)
Other Insights
Data Quality – Key to superior Procurement Performance
Businesses today, increasingly demand more sophisticated insights from procurement and supply chain functions, but significant barriers exist, primarily with the...
Effectively Managing Contingent Workforce in Software Industry
Over last decade half the contingent workforce has become increasingly important and a strategic part of the total workforce of...
Business Risk Management – Look Beyond Contract Compliance Tools
In the world of contracts management two trends are running parallel, however a meaningful common solution is not in sight...
Supply Chain Agility – Need of the Hour
In a continually volatile marketplace that we experience today, Agile Supply Chain is not an option but a necessity for...




